


In the bustling landscape of the technology industry, where innovation and competition intertwine, few names have emerged with the clout and influence of Meta, the parent company of social media giants like Facebook and instagram. But behind the sleek interfaces and digital connections lies a web of allegations that threaten to reshape the future of the digital marketplace. As the echoes of antitrust concerns reverberate through courtrooms, Meta’s monopoly trial serves as a critical juncture in the ongoing dialogue about power, competition, and consumer rights in the age of the internet. This article distills the complexities of the trial into a concise overview,unraveling the key arguments,players,and implications that could redefine the very fabric of online engagement and the future of tech regulation. Join us as we unpack “Meta’s Monopoly Trial in a Nutshell,” shedding light on the pivotal moments and stakes at play in this landmark case.
As Meta navigates its high-stakes trial regarding alleged monopolistic practices, understanding the underlying legal framework is crucial. This landmark case highlights concerns from various stakeholders, including government regulators, smaller competitors, and consumers. The trial examines whether Meta has engaged in anti-competitive behavior, particularly through its acquisition strategies, leading to a monopoly in the social media space. The outcomes could reshape the company’s operational structure and redefine market competition, serving as a pivotal moment in digital marketplace regulations.
Two primary legal theories underpin the allegations against Meta: monopolization and attempted monopolization. To better understand these concepts,consider the following factors that courts often evaluate:
| Aspect | Monopolization | Attempted Monopolization |
|---|---|---|
| Market Power | exerting notable control over a market | intent to achieve market control |
| Anticompetitive Practices | Establishing barriers for competitors | Actions that may threaten competition |
| Consumer Harm | Reduced consumer choices or increased prices | Potential future harm to consumers |
Throughout the trial,the court will also assess whether Meta’s actions have negatively impacted innovation within the social media industry. A verdict against Meta could not only impose penalties but also set precedent for how technology companies are regulated moving forward. The implications of this trial extend far beyond Meta alone, influencing the broader economic landscape of digital platforms and user data privacy.
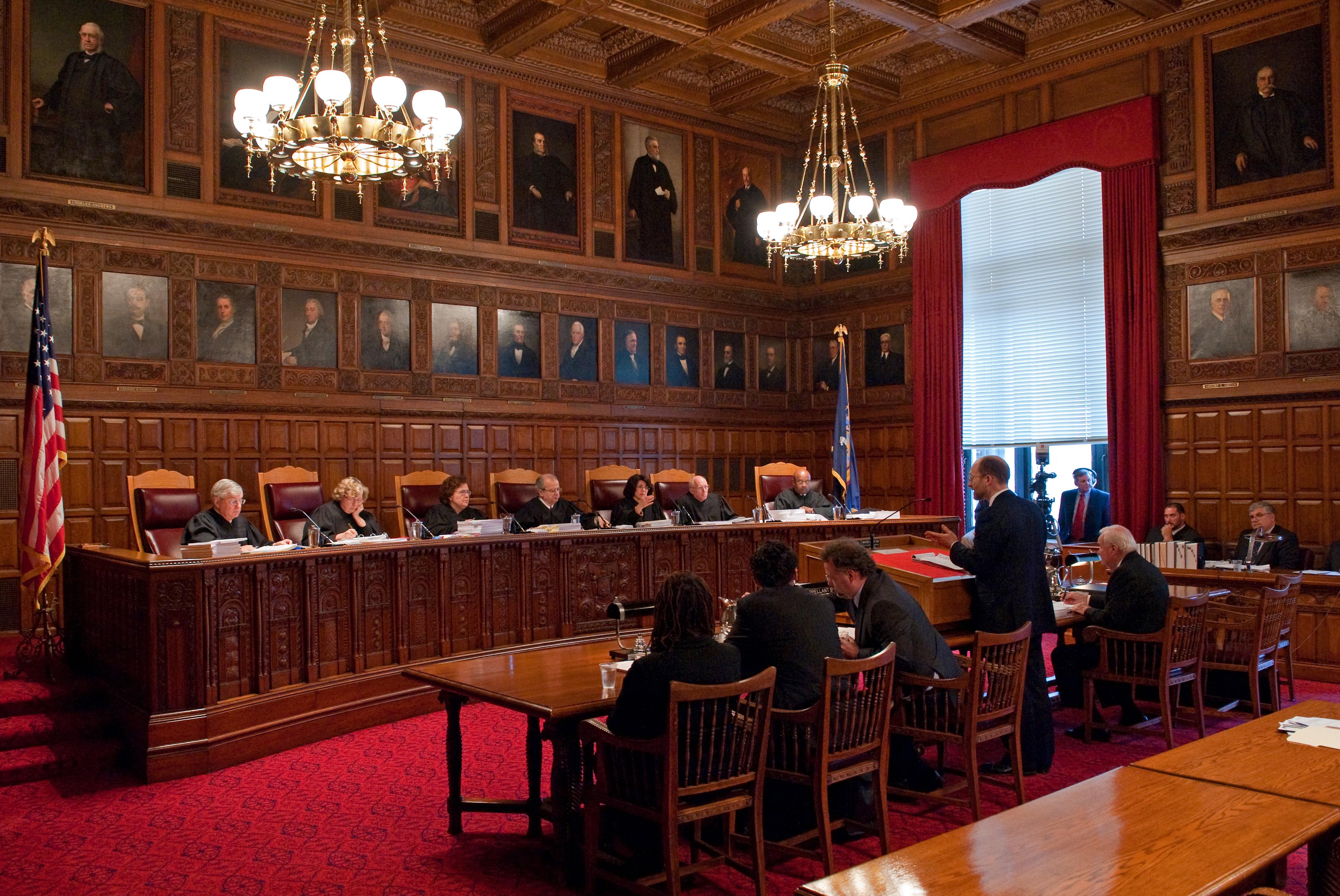

The trial against meta unfolded with compelling testimony and documentation highlighting the intricacies of its alleged monopoly in the social media landscape. The prosecution emphasized three main arguments that set the stage for a thorough examination of Meta’s business practices:
In counterarguments, Meta’s defense team presented evidence aimed at dismantling the prosecution’s assertions. They focused on three key points to support their case:
| Aspect | Prosecution Argument | Defense Argument |
|---|---|---|
| Market Influence | Meta’s control stifles competition | Consumers can freely choose alternatives |
| Acquisition Practices | Acquisitions designed to eliminate threats | Investments spur ongoing innovation |
| Data handling | Misuse of data to reinforce market power | Complies with regulations |

The outcome of Meta’s monopoly trial carries significant weight in shaping future digital competition. If the court rules against Meta, it could pave the way for stricter regulations regarding antitrust laws, particularly in the tech sector. Companies may need to reevaluate their growth strategies and consider the sustainability of their market positions. A ruling in favor of heightened scrutiny may led to:
Moreover,a potential reevaluation of how data privacy and user control are managed could emerge from this trial.As digital marketplaces become increasingly intertwined with everyday life, the need for fair access and equitable practices becomes paramount. If the outcome encourages transparency,it may lead to:
| Potential Outcomes | Impact on Users |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Privacy Regulation | Users gain better control over personal data. |
| Increased Fair Competition | More choice for consumers in digital services. |
| Greater Accountability | Companies held responsible for monopolistic practices. |

In the increasingly complex landscape of technology, companies must adopt comprehensive strategies to ensure compliance with regulations while fostering ethical practices. Embracing a proactive approach can significantly mitigate risks associated with monopolistic behaviors, as seen in high-profile cases like Meta’s recent trial. Essential tactics include:
Moreover, organizations can leverage technology to enhance their compliance frameworks. Utilizing data analytics and AI can streamline monitoring processes and help detect non-compliant activities early. By establishing clear guidelines and a culture of accountability, companies can create a foundation for ethical behavior. Key strategies include:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Risk Assessment | Identify potential compliance risks and develop strategies to address them. |
| Third-Party Management | Establish standards for evaluating the compliance of vendors and partners. |
| Whistleblower Programs | Create secure channels for reporting unethical behavior without fear of retaliation. |
As the curtain falls on the proceedings of Meta’s monopoly trial, the implications of the case linger in the air like a charged atmosphere before a storm. This legal saga, rooted in the intricate dance between innovation and competition, encapsulates the complex relationship between tech giants and the regulatory frameworks that govern them. While the trial may draw to a close, the conversations it has sparked about monopolistic practices, consumer welfare, and the future of digital marketplaces are just beginning. As we await a verdict, one thing is certain: the fallout from this trial will shape the landscape of technology and regulation for years to come, prompting both industry leaders and regulators to reconsider what it truly means to foster a fair and competitive market in an increasingly digital world. Whether we emerge from this trial with clearer guidelines or a call for reevaluation remains to be seen, but the need for dialogue has never been more pressing.