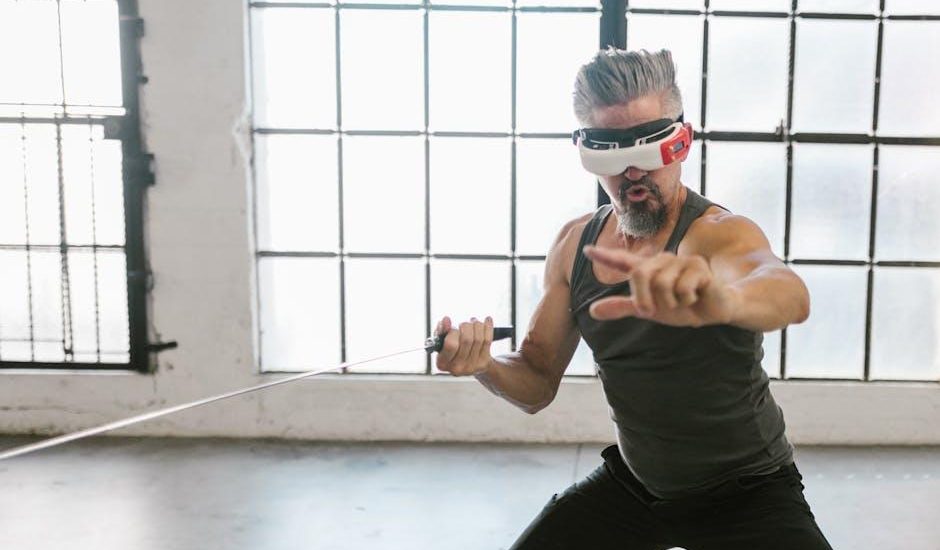



In a rapidly evolving digital landscape, where the boundaries between reality and virtuality continue to blur, Meta’s venture into virtual reality has experienced both meteoric highs and disheartening lows. Once hailed as the next frontier of human interaction, the company’s ambitious foray into the realm of immersive experiences is now shadowed by mounting financial losses and a diminishing public interest. As Meta guts its virtual reality division, the question arises: what lessons can be gleaned from a journey that promised to reshape the way we connect, collaborate, and create? This article delves into the factors contributing to Meta’s strategic retreat, exploring the complex interplay between innovation, expectation, and market reality in the ever-shifting world of technology.
In recent months, Meta has undertaken a notable reevaluation of its virtual reality (VR) business, leading to a strategic pivot that many analysts view as necesary amid ongoing financial pressure. Once viewed as a key player destined to reshape interaction in digital spaces, the VR division has suffered from decreasing user engagement and escalating costs. as the initial excitement around VR technologies has waned,Meta’s decision to scale back its ambitions reflects a calculated response to the stark realities of the market.This shift not only marks a change in product focus but also an internal reassessment of priorities within the company.
Key elements driving this realignment include:
This strategic shift signals a broader trend within tech companies that once latched onto the promise of VR. As Meta refines its portfolio, the industry watches closely to see how these decisions will influence the future landscape of digital experiences.

The recent decision to streamline operations within Meta’s virtual reality division underscores the significant financial challenges the company faces. With increasing losses reported quarterly, the once-rosy projections for VR investments have begun to take on a decidedly grim appearance.Factors contributing to this downturn include rising production costs, diminishing user engagement, and intense competition from other tech giants. This confluence of elements raises concerns not just about profitability, but also about the long-term viability of Meta’s VR vision as enthusiasts and investors alike question the sustainability of its lavish expenditures.
As Meta navigates this tumultuous landscape, the implications of these losses extend beyond mere balance sheets. To illustrate this impact, below is a brief overview of the key areas affected:
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Consumer Interest | Declining due to high costs and limited use cases |
| R&D Budget | Potential cuts affecting innovation |
| Employee Morale | Concerns about job security may dampen productivity |

As Meta pivots away from its heavily invested virtual reality division, the company finds itself at a crossroads teetering between the remnants of its past ambitions and the vast, untapped potentials of the digital landscape. With diminishing returns from VR, there is an prospect to explore other transformative technologies that could redefine user engagement and interaction. By redirecting resources towards innovations such as augmented reality (AR), artificial intelligence (AI), and even blockchain, Meta can establish itself as a pioneer in creating a more interconnected and immersive digital ecosystem that transcends customary virtual realms.
Exploring directions beyond VR opens the door to several exciting prospects:
| Opportunity | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Augmented Reality | Enhanced user engagement through interactive overlays. |
| Artificial intelligence | Personalization that drives user retention and growth. |
| Blockchain technology | Trust in digital transactions promoting community-driven models. |

As organizations like Meta reevaluate their spending and strategy in the rapidly evolving realm of virtual reality, it’s crucial to consider actionable steps for sustaining growth in emerging technologies. Companies should rethink their innovation strategies by focusing on collaboration with diverse stakeholders, including startups, academic institutions, and research labs. By fostering partnerships that leverage different expertise, organizations can enhance product offerings while reducing the risks associated with monumental technology investments. Additionally, establishing user feedback loops early in the development process allows companies to pivot in response to market demands effectively.
Investment in sustainable practices should also be a priority. This encompasses both the environmental impact of technology production and the societal implications of tech adoption. Organizations can benefit from implementing strategies such as:
moreover, businesses must routinely evaluate their portfolio against a dynamic market landscape. Companies should consider employing data analytics to anticipate trends and refine their offerings accordingly. This proactive approach, coupled with a commitment to sustainability, can pave the way for resilient growth even in unpredictable economic climates.
As the dust settles on Meta’s decision to gut its virtual reality division, the implications for the tech landscape become increasingly clear.Tho the company’s ambitious visions for VR once dazzled enthusiasts and investors alike, the mounting losses and waning public enthusiasm have prompted a strategic recalibration. This move, while difficult, signals a broader reflection within the industry about the sustainability of such cutting-edge ventures. As companies re-evaluate their technology investments in the face of economic realities, the future of virtual reality hangs in a precarious balance. Will this be the end of the VR dream, or merely a pivot towards a more grounded approach? Only time will tell, but in the ever-evolving world of technology, flexibility and adaptation may prove to be the true markers of success.