


In a landmark decision reflecting the growing enforcement of the EU Digital Markets Act, tech giants Apple and Meta find themselves on the receiving end of a staggering €700 million fine. This hefty sum, while significant in the realm of corporate law and compliance, may seem like mere pocket change in the billion-dollar landscape these companies inhabit. As regulators tighten their grip on digital monopolies, this ruling not only underscores the challenges that big tech faces in navigating complex regulations but also raises questions about the efficacy of financial penalties in influencing corporate behavior. This article delves into the implications of the fines for Apple and Meta, the broader context of the digital Markets Act, and what it means for the future of competition in the tech industry.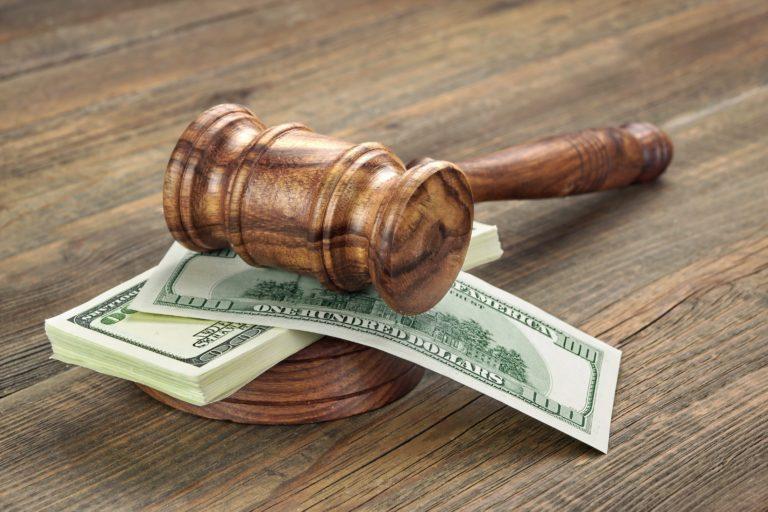
Within the colossal landscape of the tech titans, a hefty €700 million fine barely scratches the surface of what companies like Apple and Meta could be pulling in on a daily basis. For these giants, the penalties levied under the EU Digital Markets Act may feel more like a missed investment opportunity rather than a serious setback. Wealth creation in this billion-dollar industry is fueled by innovative strategies and user engagement,making regulatory costs a mere blip on their financial radar.Companies like these ofen view fines as the cost of doing business rather than as deterrents that could perhaps alter their operational strategies.
The economic impact of such fines is further underscored when we consider the sheer scale of revenue generated by these entities. To put it in viewpoint:
| Company | Annual Revenue (FY 2022) | fines Received | Revenue vs. Fine Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apple | €394.33 billion | €500 million | 788:1 |
| Meta | €117.92 billion | €200 million | 589:1 |
This table highlights just how minimal the impact of regulatory fines can be compared to the financial inflows that fuel their operations. With such staggering income, it is no wonder that the fines imposed for regulatory non-compliance seem trivial – they often represent less than a fraction of a single quarter’s profit. As we continue to witness the interplay between regulation and big tech,it becomes increasingly clear that even stringent penalties may serve more as a nudge than a major disruption in their business models.

The recent fines imposed on Apple and Meta underscore the shifting landscape of tech regulation in Europe, particularly under the EU Digital Markets Act (DMA). This landmark legislation aims to promote fair competition by imposing stringent guidelines on major tech companies considered “gatekeepers.” The hefty €700 million penalty, while ample, serves a dual purpose: it acts as a deterrent and reinforces the EU’s commitment to safeguarding consumer interests. In this evolving regulatory habitat, companies must reassess their compliance strategies to avoid similar fate and face further escalating fines that could potentially affect their operations across the continent.
As the implications of the DMA unfold, it is crucial for industry players to understand its core tenets. Key components include:
Failure to comply with these regulations not only risks financial penalties but also tarnishes reputations in an increasingly scrutinizing market. As the EU sets a precedent with these fines, other regions may follow suit, prompting a broader reevaluation of business practices for tech giants worldwide.

In a world where technology giants dominate the digital landscape, the recent €700 million fines imposed on Apple and Meta signify more than just a financial penalty; they illustrate the tightening grip of regulatory frameworks like the EU Digital Markets Act. While this sum may seem inconsequential to these billion-dollar companies,it serves as a stark reminder of the evolving compliance landscape. Both organizations must now reassess their operational strategies and rethink how they align their business practices with emerging regulations. This adjustment may involve:
As both companies brace for more rigorous oversight, their ability to navigate compliance challenges will be pivotal to maintaining market dominance. The risks associated with regulatory non-compliance are far-reaching, potentially impacting revenue streams and shareholder confidence. Navigating this complex terrain requires not only a commitment to compliance but also a proactive approach to policy engagement. Here’s a speedy look at some key compliance statistics:
| Company | 2023 Fine (€) | Compliance Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Apple | €400,000,000 | Reevaluating App Store algorithms |
| Meta | €300,000,000 | Strengthening data privacy frameworks |

To navigate the ever-evolving landscape of regulatory frameworks, tech giants should consider adopting a multi-faceted approach to enhance their relationships with regulators. Engagement and dialog are key; companies can establish dedicated teams that focus exclusively on regulatory outreach. This team should foster ongoing communication by hosting workshops, roundtables, and public consultations, which will not only educate regulators but also provide insights into the tech industry’s complexities. Obvious reporting practices can also mitigate compliance risks, ensuring that potential issues are addressed before they escalate into significant penalties.
Along with proactive engagement, investing in long-term partnerships with governments and regulatory bodies can yield substantial benefits. by prioritizing collaborative innovation, companies can work with regulators to develop frameworks that promote both growth and compliance. Proactive participation in shaping legislation, through think tanks or advisory boards, allows tech companies to influence policies favorable to their operations while demonstrating a commitment to ethical standards. Furthermore, tech giants could benefit from leveraging data analytics to showcase how their practices support public interests, thus aligning their business objectives with regulatory expectations and creating a mutually beneficial ecosystem.
the hefty fines levied against Apple and Meta serve as a striking reminder of the evolving landscape of digital regulation. With a staggering total of €700 million, these penalties may seem monumental to the average observer, yet in the grand tapestry of corporate finance, they amount to merely a ripple on the surface of vast wealth. As the EU Digital Markets Act continues to reshape the parameters of competition and consumer rights, it poses crucial questions about accountability in the tech giants’ realm. Will this serve as a wake-up call for even the most powerful players, or will it simply be absorbed as another cost of doing business? Only time will tell. As we watch this digital drama unfold, we are left to ponder the balance between innovation, regulation, and the duty that comes with immense influence.