


Introduction
In the realm of public health, few interventions hold as much potential to safeguard both maternal and infant health as vaccination during pregnancy. As expectant mothers navigate the myriad challenges of prenatal care, the timely uptake of recommended vaccines plays a crucial role in fortifying the immune defenses of both themselves and their unborn children. However, despite the proven benefits of these interventions, vaccination rates among pregnant women frequently fall short of public health targets, revealing a complex interplay of factors that influence decision-making and access.
This article embarks on a systematic exploration of the current landscape of interventions aimed at increasing vaccine uptake during pregnancy. By synthesizing findings from a range of studies through a rigorous meta-analysis, we aim to uncover effective strategies that not only address barriers to vaccination but also empower expectant mothers with the knowledge and support needed to protect their health and that of their future children. through this extensive review, we seek to illuminate pathways that can enhance vaccine acceptance and coverage, ultimately contributing to healthier communities and improved maternal and infant health outcomes.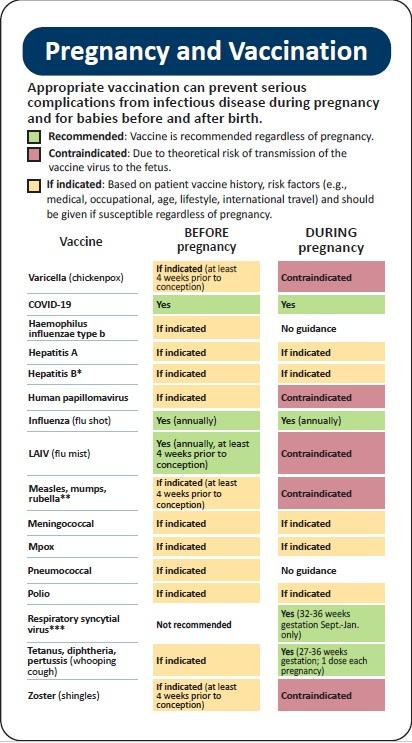
Vaccination during pregnancy serves as a vital shield for both the mother and the developing fetus, considerably reducing the risk of severe complications associated with various infectious diseases. Pregnant women are especially vulnerable due to the physiological changes that occur in their immune systems, making them more susceptible to infections. By receiving recommended vaccines, they not only protect themselves but also transfer immunity to their unborn child, ensuring a healthier start to life. Key vaccines, such as those for influenza and Tdap, have been shown to reduce the incidence of maternal illness and improve neonatal outcomes.
Despite the proven benefits, the uptake of vaccines during pregnancy remains suboptimal in some populations. This can be attributed to several factors, including misinformation about vaccine safety, lack of access to healthcare, and cultural beliefs surrounding immunization. To address these barriers, effective interventions are essential. Strategies may include:
Implementing these interventions can significantly enhance vaccine uptake, protecting both mothers and their babies from preventable diseases.A systematic review of the existing literature reveals several successful approaches:
| Intervention Type | Effectiveness (%) |
|---|---|
| Educational Workshops | 40 |
| Provider Reminders | 30 |
| Community Mobilization | 25 |
By adopting a multifaceted approach to increase awareness and access, we can significantly improve vaccination rates among pregnant women, leading to healthier outcomes for families and communities alike.

In understanding the landscape of maternal immunization, various interventions have proven effective in increasing the uptake of recommended vaccines during pregnancy. Through rigorous analysis, several strategies stand out, each with distinct mechanisms and target audiences. Some of the most impactful interventions include:
Furthermore, a meta-analysis reveals that combining these approaches significantly enhances effectiveness. For optimal results, specific populations may benefit from tailored interventions.As an exmaple:
| Target Group | Recommended Intervention |
|---|---|
| Teen Mothers | Peer-led workshops focusing on relatable experiences. |
| Low-Income Families | Incentive-based mobile clinics providing free vaccinations. |
| High-Risk Areas | Community health outreach programs offering personalized home visits. |

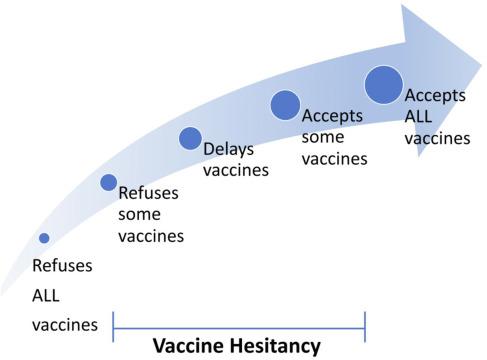
The landscape of vaccine uptake among expectant mothers is fraught with complexities that hinder public health initiatives. Misinformation plays a significant role in this context, as many individuals rely on unverified sources for health-related advice, leading to confusion about the safety and importance of vaccines during pregnancy. There are also cultural beliefs and perceptions of risk that can result in reluctance to vaccinate.Factors such as inadequate access to healthcare services, especially in marginalized communities, further exacerbate the issue.Expectant mothers may face practical barriers, including mobility issues and financial constraints, which delay or prevent them from receiving recommended vaccinations.
To understand these challenges better, it is indeed essential to examine the various factors influencing vaccine acceptance and the effectiveness of targeted interventions. A systematic review revealed several key themes:
Through strategic interventions that address these barriers, health authorities can enhance the vaccination rates among expectant mothers, ensuring better health outcomes for both mothers and their infants.
To effectively enhance vaccine acceptance and administration among pregnant individuals, a multifaceted approach is essential.Engaging educational campaigns that focus on the benefits of vaccination during pregnancy can significantly shift public perception. Such initiatives should leverage trustworthy sources and incorporate testimonials from healthcare professionals and satisfied patients. Strategies may include:
Additionally,improving access to vaccines in prenatal care settings is crucial. Implementing systems that allow for on-site vaccine administration can reduce barriers faced by expectant mothers. health providers might also consider scheduling vaccination appointments during routine prenatal visits,thereby optimizing time efficiency for both patients and clinicians. Promoting an environment of support and reassurance can further alleviate anxieties about vaccination.Key tactics may encompass:
this systematic review and meta-analysis illuminates the multifaceted landscape of interventions aimed at enhancing vaccine uptake during pregnancy. By synthesizing evidence from diverse studies, we uncover not only the successes but also the challenges faced in promoting maternal immunization. The insights gleaned from this analysis underscore the importance of tailored strategies that resonate with the unique experiences of expectant mothers.as we move forward, the findings serve as a crucial guide for healthcare providers, policymakers, and public health advocates alike. Together, we can harness this knowledge to foster an environment where every pregnant individual feels empowered to protect both their health and the wellbeing of their child through vaccination. The journey towards higher vaccination rates begins with informed action, and with continued research and collaboration, we can make significant strides in safeguarding maternal and infant health.